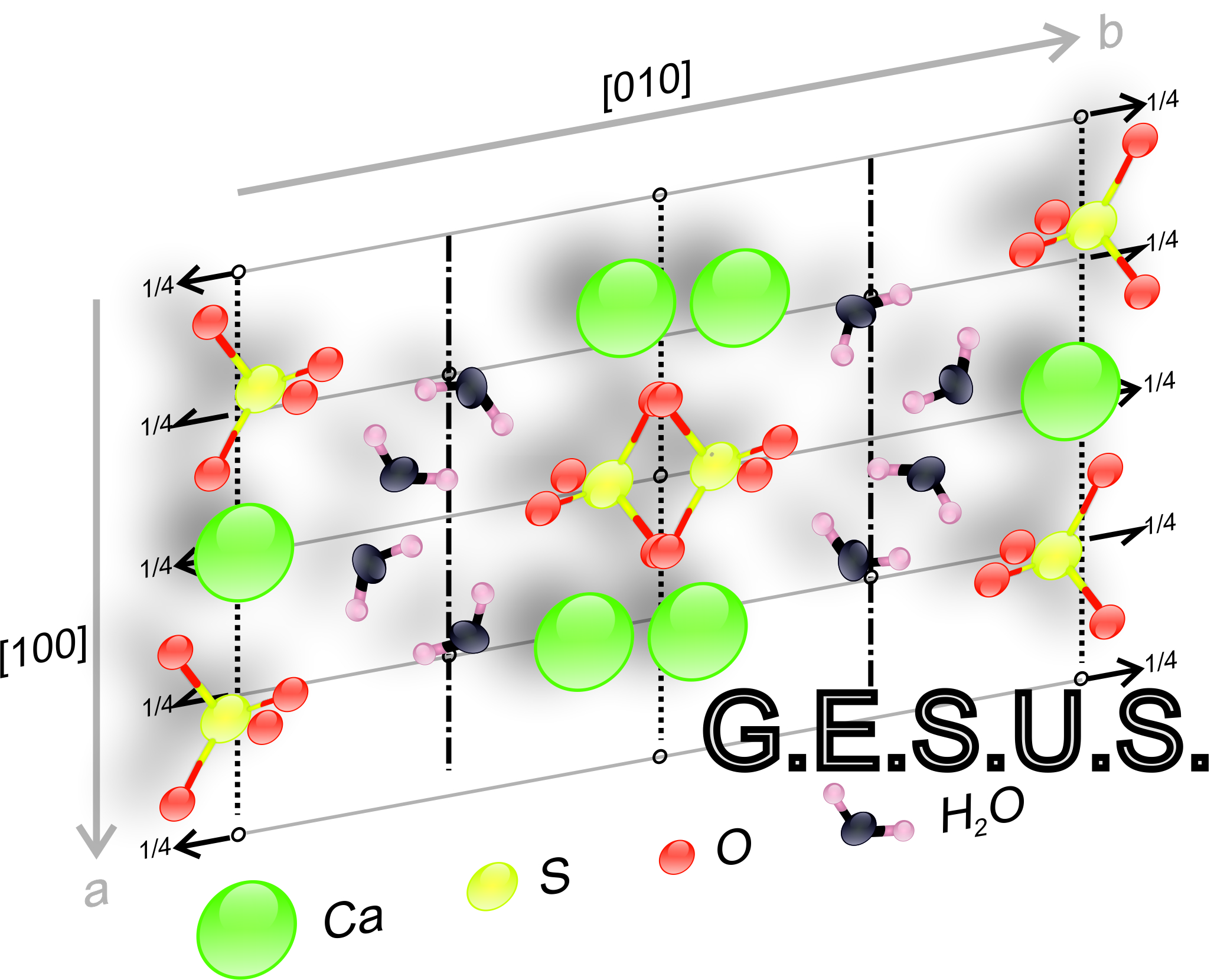
Motif: A set of atoms containing a cell that is periodically repeated.
Structure: Refers to the distribution and arrangement of the internal components (atoms, ions or molecules) of crystalline solids. It would be the combination of the motif and the lattice.
Reticular multiplicity: Number of nodes per cell (considering the sharing of nodes in adjacent cells).
Primitive cell: A cell that has only one node (it is limited by unit vectors and its multiplicity is always one).
Multiple cell: A cell that has more than one node (it contains "extra" vectors in addition to the unit reference vectors and its multiplicity is greater than one). The area (2D) or volume (3D) of a cell is proportional to its multiplicity. (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Types of 3D-lattices:
P (primitive)
I (body centered)
C (base centered C)
F (face centered)