Reticular Theory
For study and classification of the structures of crystalline materials, their symmetry is considered based on theoretical lattice models, which represent the ideal crystal. (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.- Comparison between structure and lattice
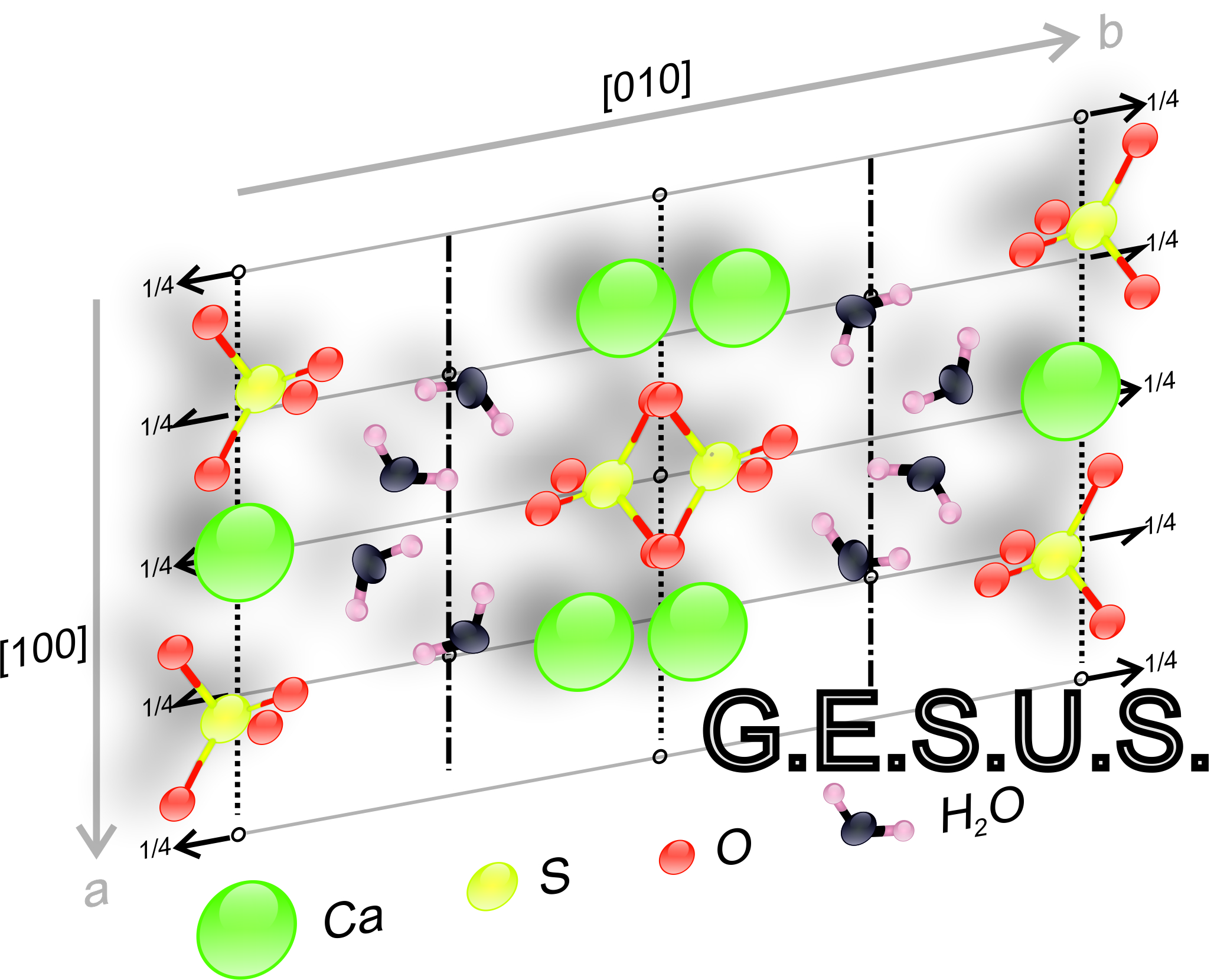
lattice: a three-dimensional arrangement of nodes, defined by a system of three non-coplanar vectors and the angles between them.
node: mathematical entity representing the atomic distribution around a point. It represents the basic unit of repetition in a structure, i.e. the minimum set of repeating atoms, ions or molecules in a structure.
A periodic medium can be represented through a grid of nodes connected by vectors that can form a series of parallelograms (2D) or parallelepipeds (3D) juxtaposed to form a lattice.
unit cell: each portion of the lattice composed only of nodes linked by the non-equivalent minimum (2D)- or (3D)-vectors. They represent, as well as the nodes, periodically repeating units (one or many atoms).